Car Seat belts often called safety belts, that are designed to protect passengers from serious injuries in the case of a crash. The main purpose of seat belts is to keep the occupant from hitting the windshield or dashboard and avoiding deaths and reducing injuries. They can’t do their job well, though, until they’re used. Here in this article, we will learn about how to use seat belts and how seat belts work in a car.
Seat belts protect against major accidents:
Seat belts help to protect against injuries in the case of car accidents by lowering the velocity of a body. Because the body experiences a rapid decrease in its speed due to the seat belt. A passenger in a vehicle will keep moving ahead until the car has come to a complete stop due to inertia, which is the body’s resistance to a change in speed or direction of travel.
If a car traveling at 50 mph collides with a tree, its velocity is instantaneously reduced to zero. Then the passenger will continue to move ahead at the same speed unless something in front of them creates a stopping force. Seat belts slow us down by counteracting this inertia. When driving in a car, ensure sure you are constantly wearing your seat belt. You should always fasten the Seat belts.
Seat Belts Working:
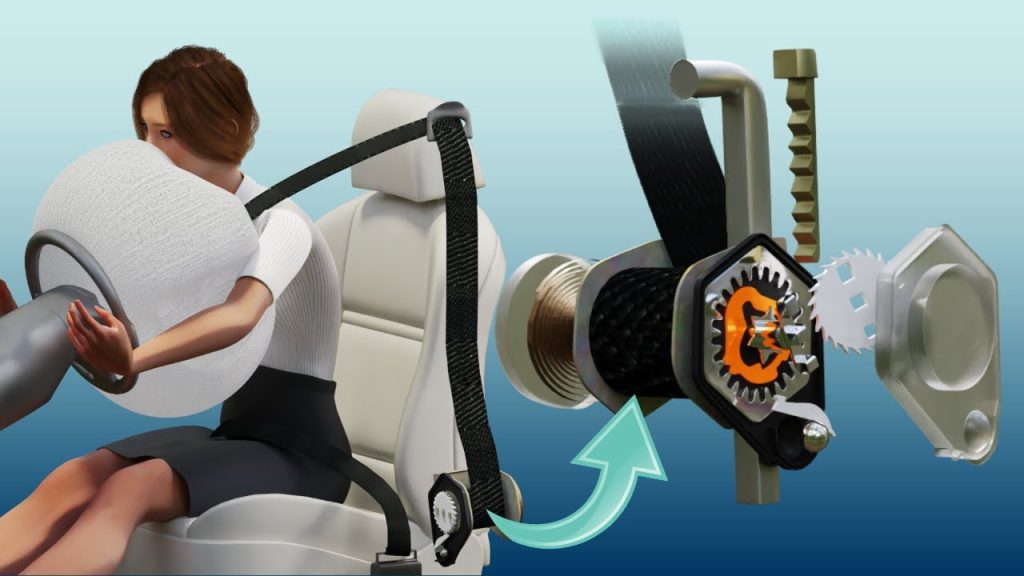

Three-Point Retractable Lap and Shoulder seat belt working consists of a Retractor device and locking mechanism. This is the most typical seat belt system for passenger cars around the world. Let’s see how seat belts work?
Seat Belt Retractor Mechanism:
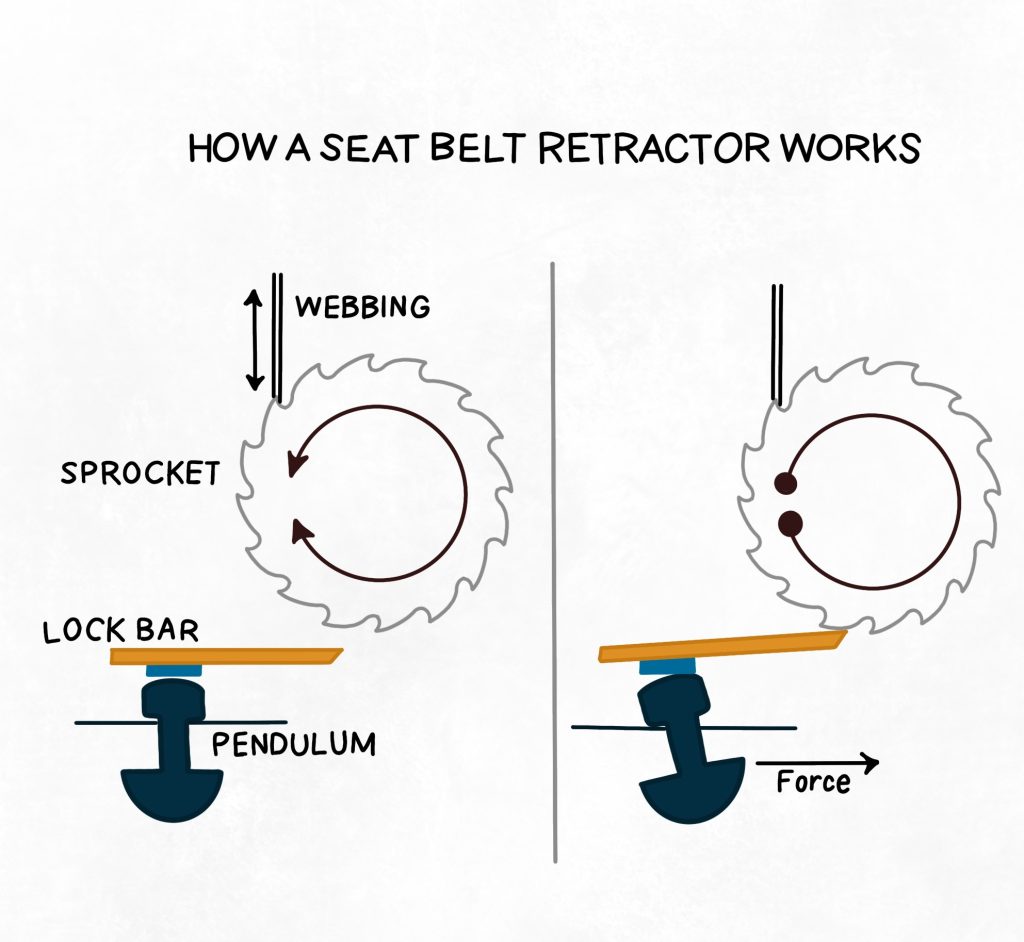
A seatbelt is made up of a flexible webbing belt and a retractor device. The retractor consists of a spool, around which the belt winds. The spool is the essential component of the retractor mechanism. A spring is attached to the spool to keep the webbing taut. It is normally housed inside a plastic enclosure over the passenger’s outer shoulder. The spool spins counter-clockwise as you pull a seatbelt across your chest and pelvis, untwisting the spring. When you let go of the belt, the spring causes the spool to spin clockwise, as it seeks to return to its coiled state. It also spins in a clockwise direction till the webbing is completely slack.
Spool Locking systems:
The spool of the looking system is now locked using two sensors instead of one. The first is a sensor that senses vehicle deceleration. The second is the webbing sensor to detect any rapid deceleration in the vehicle. When anything jerks the belt webbing, the spool locks. The speed of the spool rotation provides the activation force in most configurations.
Spool Locking Mechanism:

The spool’s locking mechanism is the most important part of a seat belt. The looking system ensures that the belt stays tight in the event of an accident. The retractor contains a locking mechanism that prevents the spool from turning in the case of a collision. The primary purpose of a locking system is to prevent the occupant from being thrown towards the dashboard by keeping the spool from turning.
The seat belt activated system consists of centrifugal force, a lever attached to the spool, lever that activates a device that grips the tooth gear. The spool is locked using a centrifugal clutch system. The centrifugal lever does not pivot when the spool turns slowly. When the spool rotates violently, the lever’s centrifugal force overcomes the spring force, and the clutches lock onto the spool’s teeth.
Pre-tensioners:
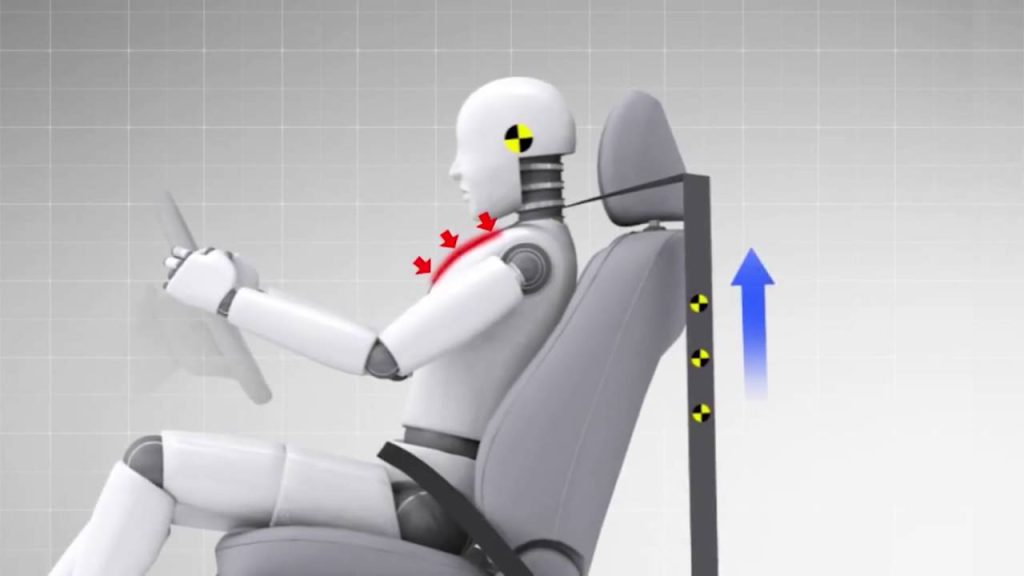
In some Modern seat belts mechanism, a pre-tensioner is used to tighten the seat belt webbing. standard seat belts the locking mechanism only locked the spool’s rotation completely. When a collision happens, a pre-tensioner retracts a portion of the webbing of a seatbelt, tightening the seatbelt to restrain people rapidly and minimizing the amount they are propelled forward in a moderate or severe frontal accident. Load limiters help prevent passengers from injuries caused by seatbelts.
Pyrotechnics are used by modern pre-tensioners to pull the belt in. A separate gas chamber with an igniter substance is included. The igniter material is ignited by flowing electric current through it when the sensor senses a collision. A central processor detects the collision and transmits the electric current to the igniter. The ignition pushes the piston upward by releasing gases at high pressure. The top of the piston has a rack gear that moves up and interacts with the spool gear, rotating the spool hard to pull the belt inside.
Fasten Seat Belt Correct:

You should always fasten your seat belt correctly. However, if a seat belt is not utilized properly, it will not give full protection. The following are the key elements of proper seat belt fitting.
The shoulder seat belt must be across the shoulder through the neck and arm. The belt should never be folded under an arm or behind the back. otherwise, it will not be able to restrict the upper body in the event of a collision. The lap belt should be lower as possible at least touching the thighs. so that the distributed crash forces to the strong hip bones rather than the fragile abdomen area.
The shoulder and lap belts should both fit the whole body without any loosening. If the lap belt is excessively loose, the occupant can submarine under the lap belt.
Is Seat Belt Effective Way To Avoid Injuries?

according to The Royal Society for the Prevention of Accidents (ROSPA), Ever since it became mandatory to fasten seat belts in 1983. it helped to save 50,000 lives, 590,000 serious casualties, and 1.5 million minor injuries. it is true that you have a 1 in 84 probability of dying in a car accident. On the other hand, the usage of a seat belt reduces this figure by 50%. This indicates that wearing a seatbelt is critical for avoiding harm in a car accident.





